What is Hashing ?
Hashing is a technique used to store elements in such a way that searching over them should be very fast. It internally uses a Hash Table to store the elements.
What is Hash Table ?
Hash Table is a kind of Data Structure Used to achieve Hashing. It internally maintains a an array of Buckets. Where each bucket can store multiple elements and mapped to Hash Code. This hash code is calculated using Hash Function.
Now let’s see how Hashing works suning Hash Table,
Inserting an element in Hash Table
Whenever an element is inserted in Hash Table then first its hash code is calculated and based on its hash code it’s decided that in which bucket it will be stored.
Let’s understand this by an example,
For example, we want to store some numbers in a Hash Table i.e.
12, 23, 56, 67, 89, 43
This Hash Table will internally use 10 Buckets i.e.
Our Hash Function that will return the Hash Code will be,
Hash Code = Element value % 10
This Hash code for,
12 will be 2
23 will be 3
56 will be 6
67 will be 7
89 will be 9
43 will be 3
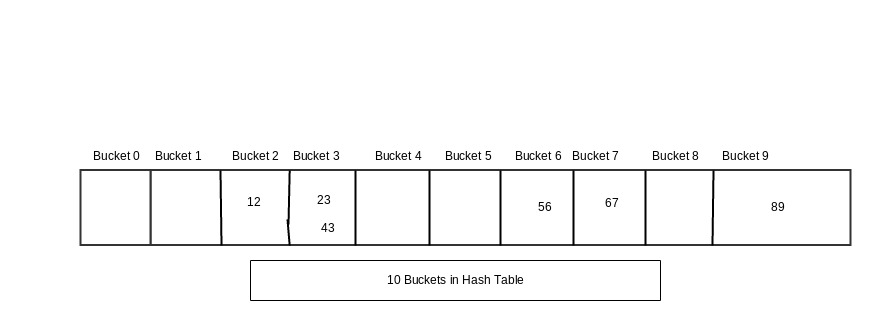
Now Using this hash code for each element it will be decided where that element will be stored i.e. 12 will be in bucket 2 because its hash code is 2. Similarly where all elements will be stored in the bucket corresponding to their hash code i.e.
Collisions in Hashing
Now as we can see hash code of both 23 and 43 is same i.e. 3. This is called Collision in Hashing. In case of collision both the elements will be stored in same bucket.
Searching an element from Hash Table
Now when we want to search for an element in hash table then first we will calculate that element’s hash code. Then on the basis of hash code we will directly go to the bucket where this element will be stored. Now in that bucket there can be multiple elements, in such case we will search our element in those elements only.
Suppose in above example we want to search 67 from the hash table.
Then first we will calculate its hash code and that will be 67 % 10 i.e. 7.
Then we will go to bucket no. 7 directly and look for the element in it.
Calculating Searching time in Hash Table
Best case
If each bucket contains only one element in Hash table then that is a best case from searching perspective. Searching time in such scenario will include following effort,
Calculating hash code is of complexity O(1)
[showads ad=inside_post]
If there is only one element in bucket then selecting element from Bucket is of complexity O(1)
Hence Searching for an element in best case will be of complexity O(1)
Whereas, in case of collision i.e. multiple elements in bucket complexity will be O(no. of elements in bucket) but that will be much lesser than O(n) complexity i.e. searching element from a List.
Worst Case in Hashing
Worst case in hashing will happen if Hash Function is not implemented properly i.e. its producing same hash code for many element.
Suppose our hash function is as follows,
Hash code = element / 100
Then in above example, hash code for all elements i.e 12, 23, 56, 67, 89, 43 will be 0. Hence, all elements will be stored in bucket 0.
In such scenario complexity will be worst because all elements are in same bucket. So, complexity will be O(n) because it has to search for required element from all elements.
Pingback: std::unordered_set Basic Usage & Example – thisPointer.com
Pingback: Unordered_map Usage Tutorial and Example – thisPointer.com
Hi, David Mayer here from java8certificationquestions.com.
Very deep explanation of how hashing works in Java.
I am going to share it on my social media.
Thanks
David
Pingback: map vs unordered_map | When to choose one over another ? – thisPointer.com
Pingback: What is a dictionary in python and why do we need it? – thispointer.com