In this article, we will be discussing the differences between JOIN and UNION including examples of how to use them.
Table of Contents
Introduction
JOIN is used to retrieve data from multiple tables. Data retrieved from JOINs are horizontally aligned. A JOIN is used whenever multiple tables appear in the FROM clause of the query.
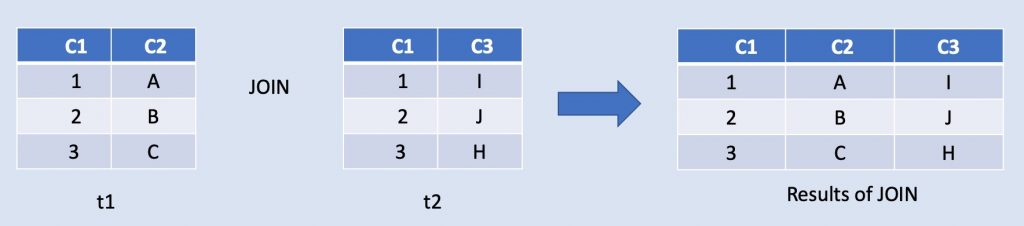
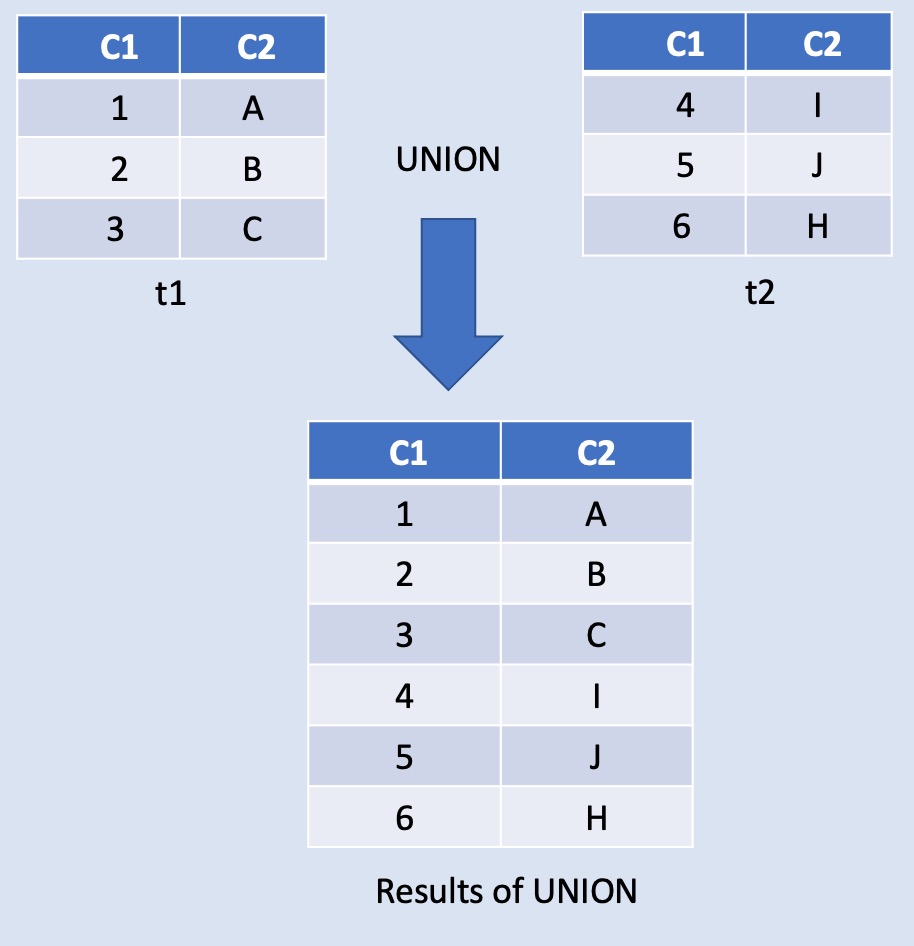
UNION combines the result from multiple SELECT statements into a single result set. Data retrieved from UNION are vertically aligned.
<div id=”two” style=”padding-top: 100px; margin-top: -100px;”></div>
Basic differences between JOIN and UNION
| JOIN | UNION |
| JOIN is generally used to combine data from different tables. | UNION is generally used to combine data from different select queries. |
| JOIN works connecting the tables based on the logical relationship between each other. | UNION works to get a single result set from multiple select queries. |
| JOIN will combine the data to get new columns. The columns from the one table are shown with columns from the other table side by side in the same row. | UNION will combine the data to get new rows. The set of rows from one table are shown above the rows from the other table. |
| It is not mandatory to have the same number of columns in both tables while doing a JOIN. | It is mandatory to have the same number of columns in select statements while doing a UNION. |
| Datatypes of the columns need not be the same while doing a JOIN. | Datatypes of the columns should be the same while doing a UNION. |
| The order of the columns need not be the same while doing JOIN. | The order of the columns should be the same while doing UNION. |
| JOIN will not remove the duplicate rows from the result. | Union will remove the duplicate rows from the result. **Note that UNION ALL will not remove duplicates. |
<div id=”three” style=”padding-top: 100px; margin-top: -100px;”></div>
Examples of JOIN and UNION
Before moving into the detailed example of each, let us peek into the data.
Frequently Asked:
- MySQL SELECT WHERE
- MySQL select row with max value for each group
- What are views in MySQL
- Reset AUTO_INCREMENT after Delete in MySQL
We assume that we have three tables, student_details, temporary_summer_students, and student_address_city, in our database with the below rows.
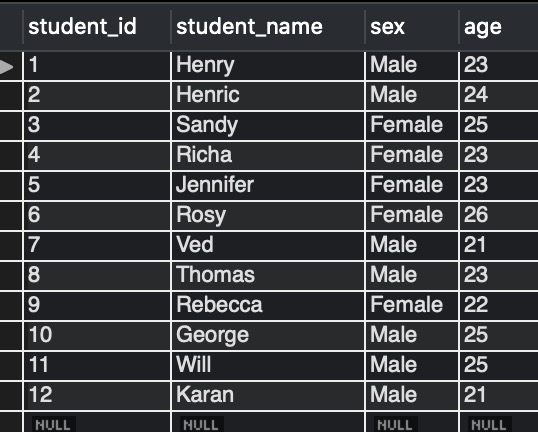
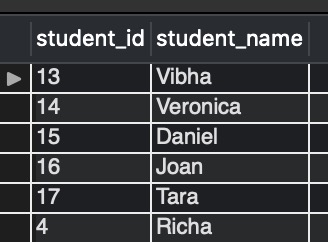
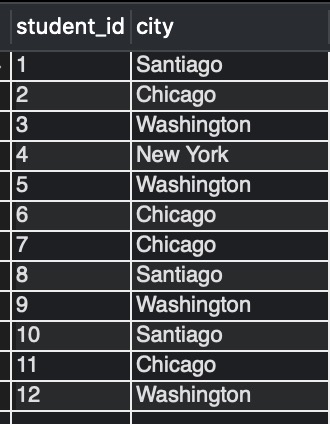
Example of JOIN
Get the details of permanent students along with their city information.
Observe the below query for the solution.
SELECT
s1.*, s2.city
FROM
student_details s1,
student_address_city s2
WHERE
s1.student_id = s2.student_id;
Action Output Message Response:-
12 row(s) returned.
Output:-
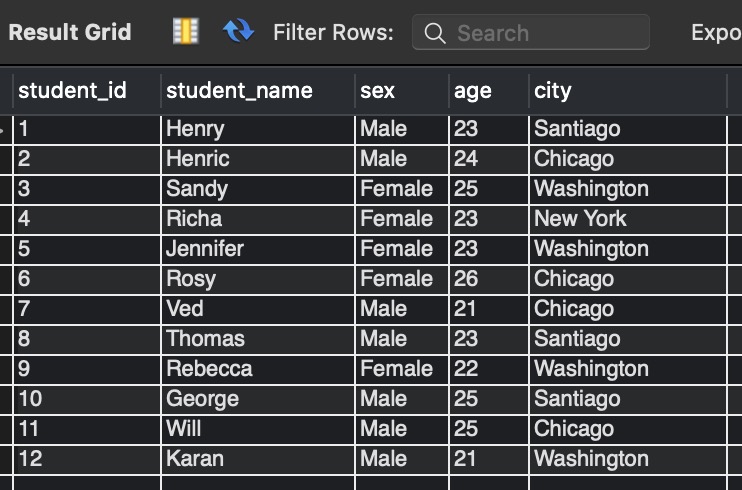
Explanation:-
In the above query, an INNER JOIN is made between student_details and student_address_city tables ON student_id. Hence we fetch student_name, sex, city from the student_details table and city from student_address_city.
Example of UNION
Get the student_id and student_name for both permanent and temporary summer students.
Observe the below query for the solution.
SELECT
student_id, student_name
FROM
student_details
UNION SELECT
student_id, student_name
FROM
temporary_summer_students;
Action Output Message Response:-
17 row(s) returned.
Output:-
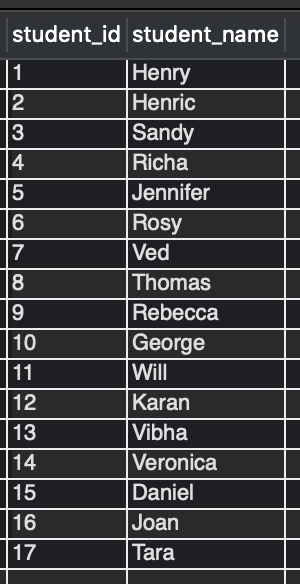
Explanation:-
In the above query, UNION is done between two SELECT statements: first, fetching the data from the student_details table and the another fetching the data from the temporary_summer_students table.
Note that the duplicate row with student_id = 4 has been removed from the final result.
We hope this article helped to understand the differences between JOIN and UNION. Good Luck!!!