This article will discuss MySQL views with a few examples of creating, updating, and dropping them.
Table of Contents:-
- Introduction to views in MySQL and usage of views
- How to create view in MySQL from single and multiple tables
- ALTER views in MySQL
- DROP views in MySQL
Let us get started by looking into the sample data tables sale_details and sale_person_designation, which we will be using to create the views. To view the snapshot of data present in both the tables, execute:
SELECT * FROM sale_details;
Output:-
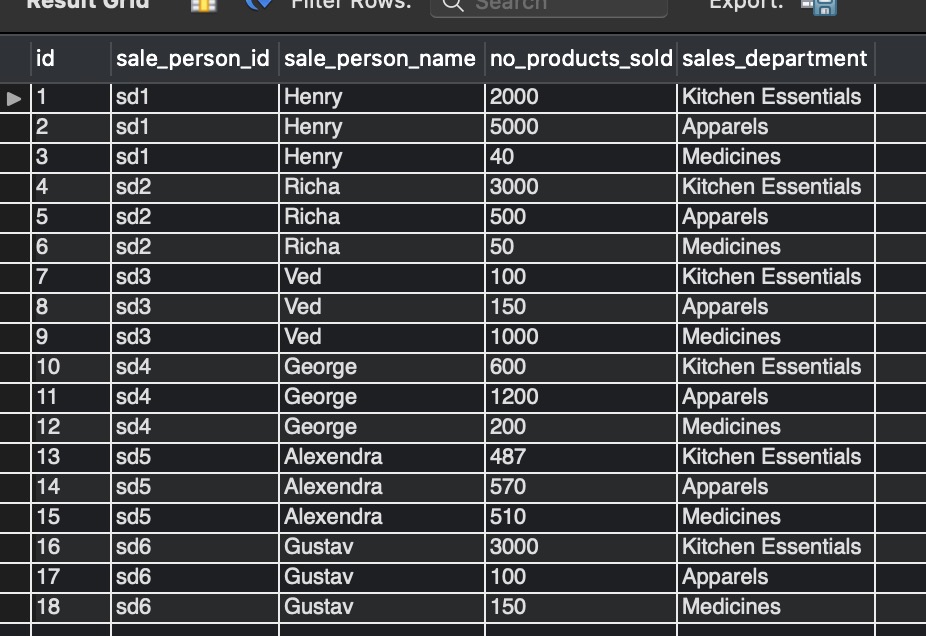
SELECT * FROM sale_person_designation ;
Output:-
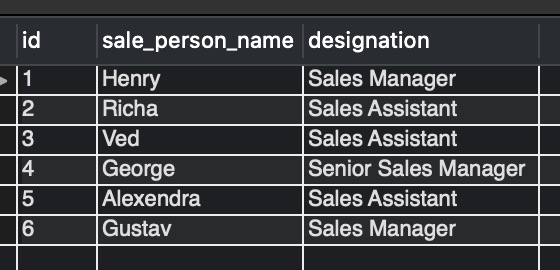
Introduction to views in MySQL and usage
A view is a virtual table that gets the data from other tables. We can also say that a view is a stored query that is invoked whenever we require the same data again from this query. These views are stored in the MySQL database and revoke a result set based on the same query. We can also involve multiple databases to create a view.
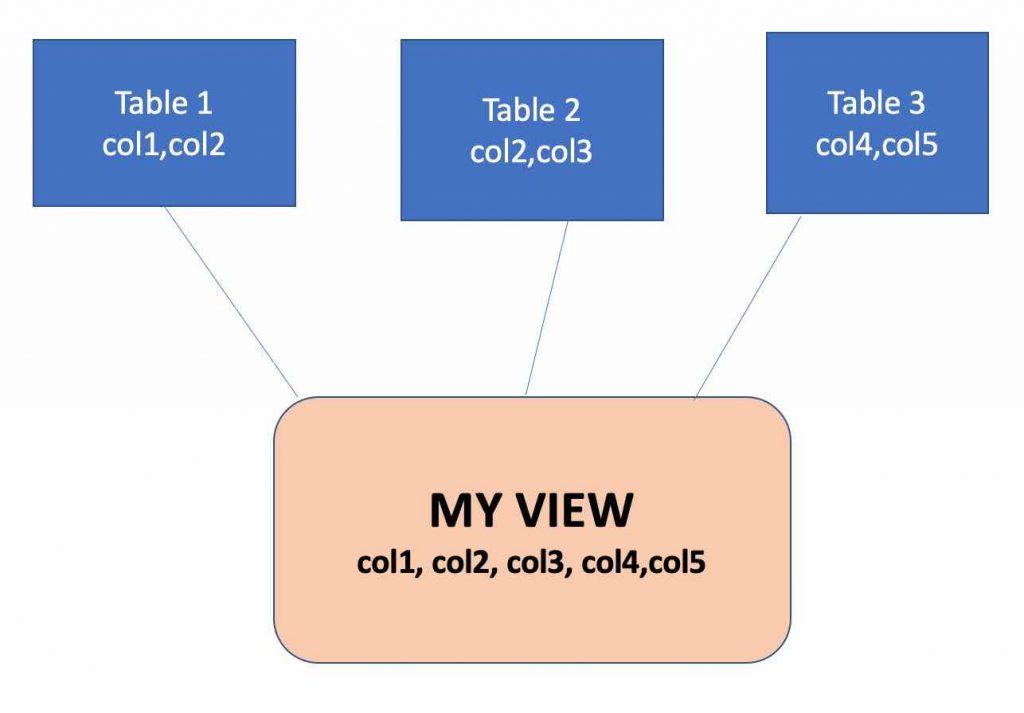
Common usage of views:
Frequently Asked:
- Count with If Condition in MySQL Query
- MySQL DELETE WITH JOIN
- MySQL select row with max value for each group
- Difference between JOIN and UNION
- Store the queries that need to be run again and again.
- In many software, views are used as virtual security tables where users should not access original tables.
- Views hide the complexity of data.
- We can use views as aggregated tables, for example, showing the result of sum() or avg() functions from a table.
- We can also use views to get any required information repeatedly for, for example, months in a year.
How to create views in MySQL from single and multiple tables
In this section, we will be creating two views using the CREATE statement, one from a single table and another one from more than one table (tables are shown above sale_details and sale_person_designation) but let us have a look into the syntax before moving ahead.
Syntax:
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW name_of_view [(column list)] AS your_query;
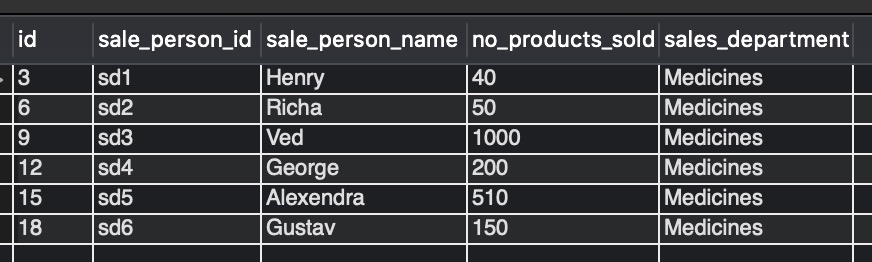
Example1: Create a view for getting the sales data for only the Medicine department.
Observe the below create view statement.
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW sale_data_medicine_v AS
SELECT
*
FROM
sale_details
WHERE
sales_department = 'Medicines';
Action Output:-

To get the data from the view sale_data_medicine_v, do select from the view.
SELECT * FROM sale_data_medicine_v;
Output:-
Example2: Create a view for getting the salesperson data including the designation
Observe the below create view statement.
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW sale_person_data_v AS
SELECT
sd.sale_person_id, sd.sale_person_name, spd.designation
FROM
sale_details sd,
sale_person_designation spd
WHERE
sd.sale_person_name = spd.sale_person_name
GROUP BY sd.sale_person_name;
Action Output:-

To get the data from the view sale_person_data_v, do select from the view.
SELECT * FROM sale_person_data_v;
Output:-

ALTER views in MySQL
If the view is already created and we want to modify the definition of the view, then we can use the ALTER statement.
Syntax:
ALTER VIEW name_of_view [(column list)] AS your_modified_query;
Example: Modify the view sale_data_medicine_v so that it gets only records with no_products_sold more than 100.
ALTER VIEW sale_data_medicine_v
AS SELECT
*
FROM
sale_details
WHERE
sales_department = 'Medicines' AND no_products_sold > 100;
Action Output:-

SELECT * FROM sale_data_medicine_v;
Output:-
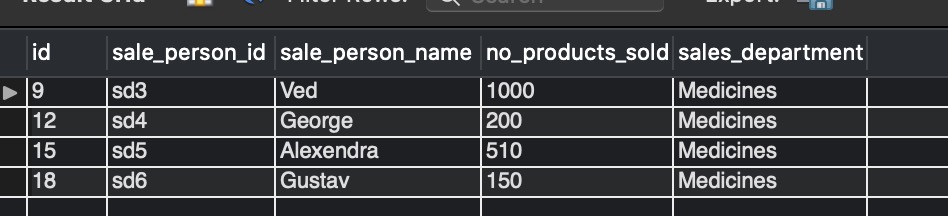
Observe the difference in image_5 and image_9.
DROP views in MySQL
This section will focus on how to drop a view in MySQL. We will be using DROP VIEW statement.
Syntax:
DROP VIEW [IF EXISTS] name_of_view ;
DROP the view sale_person_data_v.
DROP sale_person_data_v;
Action Output:-

Let us verify if the view got delete or not by executing:
SELECT * FROM sale_person_data_v;
Action Output:-

As we can see in image_11, an error is thrown: Error Code: 1146. Table ‘thispointerdb.sale_person_data_v’ doesn’t exist.
READ MORE:
- What are indexes in MySQL
- MySQL create table if not exists
- MySQL ADD COLUMN IF NOT EXISTS
- MySQL get column names
We hope this article helped you to build an understanding of views in MySQL. Good Luck !!!