We can create a temporary table in MySQL using the TEMPORARY keyword. A temporary table is a table that is visible only during the current session and hence has its scope in a single session only. Once the session is closed, access to the temporary table is closed as well.
Two different sessions can use a common name for two different temporary tables simultaneously.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES privilege is required to create temporary tables. This article talks about:
- Create temporary table and insert data.
- Create temporary table in a select statement without a separate create table.
- Create a temporary table in MySQL with an index.
- Add a column to temporary table in MySQL.
Create temporary table and insert data
We will look into the syntax for creating the table followed by an example.
SYNTAX:-
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temporary_table_name SELECT * FROM existing_table_name LIMIT 0;
Syntax shows the temporary_table_name is the name of your temporary table, and existing_table_name is the table which we are using.
EXAMPLE:-
Let us now see how to create a temporary table followed by inserting the data into it. Assuming that the table(existing_table_name) registration_status already exists in the database with the below data.
Frequently Asked:
- Inserting multiple rows in MySQL
- MySQL select row with max value
- MySQL SELECT WHERE LIKE
- MySQL Delete Duplicate Rows but keep one
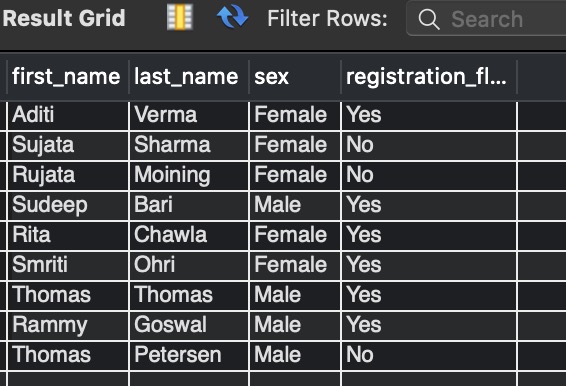
Observe the below query as an example for creating a temporary table.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE registered_data SELECT first_name, registration_flag FROM registration_status_details WHERE registration_flag ="Yes" AND sex="Female" ;
In these queries, we create the temporary table registered_data and insert the data into them from the registration_status table with the condition that data with only registration_flag = “yes” and sex = “Female” should be inserted.
SELECT * FROM registered_data;
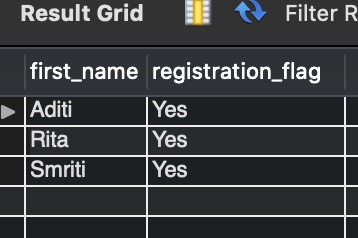
Add more data with the INSERT command. See the below query.
INSERT INTO registered_data(first_name,registration_flag) SELECT first_name,registration_flag FROM registration_status_details WHERE registration_flag ="Yes" AND sex="Male" ;
Again, SELECT * FROM registered_data to view all rows.
Create temporary table in a select statement without a separate create table
We can also create a temporary table using the AS keyword. Observe the below query.
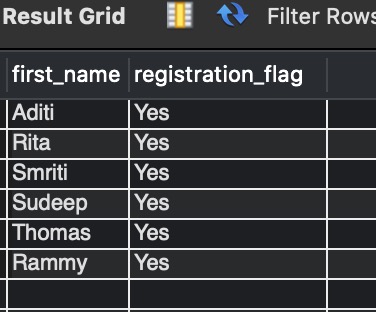
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE IF NOT EXISTS registered_data AS (SELECT first_name,registration_flag FROM registration_status_details WHERE registration_flag ="Yes");
Action Output Message: CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE IF NOT EXISTS registered_data AS (SELECT first_name,registration_flag FROM registration_status_details WHERE registration_flag =”Yes” ) 6 row(s) affected Records: 6 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 0.0024 sec
SELECT * FROM registered_data;
Output:-

Create a temporary table in MySQL with an index
In this section, we will see how to create a temporary table with an index. We will be looking into the syntax followed by an example.
SYNTAX:-
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temporary_table_name (index_column_name INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, PRIMARY KEY(index_column_name), INDEX(index_column_name)) SELECT * FROM existing_table_name WHERE <conditions> ;
The syntax shows that after providing the name of the temporary table (temporary_table_name) in the brackets we can specify the additional index column – index_column_name INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, PRIMARY KEY (index_column_name), INDEX(index_column_name)
Let us forge ahead by looking into the example query stated below.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE registered_data_with_index (registration_number INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, PRIMARY KEY(registration_number), INDEX(registration_number)) SELECT * FROM registration_status_details WHERE registration_flag ="Yes" ;
Action Output Message: 6 row(s) affected Records: 6 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 0.0014 sec
Here, we created a temporary table registered_data_with_index and added a new index column registration_number, specified with an AUTO_INCREMENT value.
SELECT * FROM registered_data_with_index to view the data in registered_data_with_index table.

To view if the index got created or not, run the below query.
SHOW INDEXES FROM registered_data_with_index;
Output:-
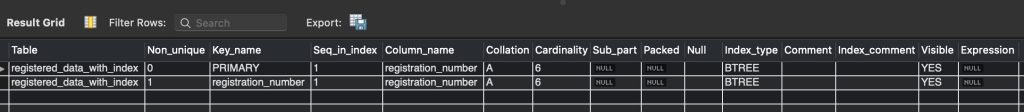
The output in figure 1.6 shows that the index got created on registration_number.
Add a column to temporary table in MySQL
We can add a column as well to a temporary table. Let us look into the syntax followed by an example.
SYNTAX:–
ALTER TABLE temporary_table_name ADD new_column_name <datatype> DEFAULT default_value;
Here in the ALTER statement we are adding a new column new_column_name to the temporary table temporary_table_name.
EXAMPLE:-
We will be using the above created temporary table registered_data_with_index and adding a new column city_name to it.
ALTER TABLE registered_data_with_index ADD city_name varchar(255) DEFAULT 'Austin';
SELECT * FROM registered_data_with_index to view the data in registered_data_with_index table.
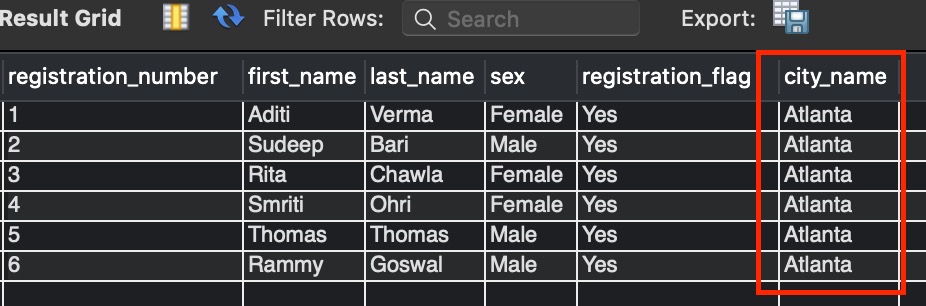
As we can see in the above image, a new column city_name got added to the table registered_data_with_index.
We hope this article provides a good understanding of creating temporary tables. Good Luck !!!