In this article we will discuss how to drop columns from a DataFrame object.
DataFrame provides a member function drop() i.e.
DataFrame.drop(labels=None, axis=0, index=None, columns=None, level=None, inplace=False, errors='raise')
It accepts a single Label Name or list of Labels and deletes the corresponding columns or rows (based on axis) with that label.
It considers the Labels as column names to be deleted, if axis == 1 or columns == True.
By default it doesn’t modify the existing DataFrame, instead it returns a new dataframe. If we want to delete the rows or columns from DataFrame in place then we need to pass another attribute i.e. inplace=True
Let’s understand by examples,
Create a DataFrame object,
Frequently Asked:
- Python Pandas : Drop columns in DataFrame by label Names or by Index Positions
- Add Row to Dataframe in Pandas
- Python Pandas : How to get column and row names in DataFrame
- Python Pandas : Count NaN or missing values in DataFrame ( also row & column wise)
# List of Tuples
students = [ ('jack', 34, 'Sydeny' , 'Australia') ,
('Riti', 30, 'Delhi' , 'India' ) ,
('Vikas', 31, 'Mumbai' , 'India' ) ,
('Neelu', 32, 'Bangalore' , 'India' ) ,
('John', 16, 'New York' , 'US') ,
('Mike', 17, 'las vegas' , 'US') ]
#Create a DataFrame object
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns = ['Name' , 'Age', 'City' , 'Country'], index=['a', 'b', 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f'])
Delete a Single column in DataFrame by Column Name
Contents of DataFrame object dfObj is,
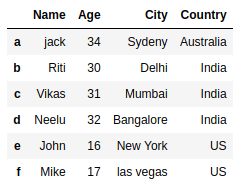
let’s delete a column ‘Age’ from the above dataframe object,
modDfObj = dfObj.drop('Age' , axis='columns')
Contents of the new DataFrame object modDfObj is,

Drop Multiple Columns by Label Names in DataFrame
To drop multiple columns from a DataFrame Object we can pass a list of column names to the drop() function.
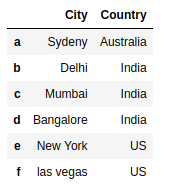
For example, drop the columns ‘Age’ & ‘Name’ from the dataframe object dfObj i.e.
modDfObj = dfObj.drop(['Age' , 'Name'] , axis='columns')
Contents of the new DataFrame object modDfObj is,
Drop Columns by Index Position in DataFrame
To drop columns by index position, we first need to find out column names from index position and then pass list of column names to drop().
For example delete columns at index position 0 & 1 from dataframe object dfObj i.e.
# Delete columns at index 1 & 2 modDfObj = dfObj.drop([dfObj.columns[1] , dfObj.columns[2]] , axis='columns')
Contents of the new DataFrame object modDfObj is,

Drop Columns in Place
Delete columns ‘Age’ & ‘Name’ from dataFrame dfObj in Place by passing inplace=True in drop() function i.e.
dfObj.drop(['Age' , 'Name'] , axis='columns', inplace=True)
It will update the contents of dfObj i.e. columns ‘Age’ & ‘Name’ will be deleted from dfObj.
Drop Column If Exists
Before delete a column using drop() always check if column exists or not otherwise drop() will throw a KeyError i.e.
# Check if Dataframe has a column with Label name 'City'
if 'City' in dfObj.columns :
dfObj.drop(['City'] , axis='columns', inplace=True)
else :
print('Column Name not found')
Complete example is as follows,
import pandas as pd
def main():
# List of Tuples
students = [ ('jack', 34, 'Sydeny' , 'Australia') ,
('Riti', 30, 'Delhi' , 'India' ) ,
('Vikas', 31, 'Mumbai' , 'India' ) ,
('Neelu', 32, 'Bangalore' , 'India' ) ,
('John', 16, 'New York' , 'US') ,
('Mike', 17, 'las vegas' , 'US') ]
#Create a DataFrame object
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns = ['Name' , 'Age', 'City' , 'Country'], index=['a', 'b', 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f'])
print("Original DataFrame" , dfObj, sep='\n')
'''
Delete a Single column in dataFrame by Column Name
'''
print("**** Delete column 'Age' in DataFrame object ****")
modDfObj = dfObj.drop('Age' , axis='columns')
print("New DataFrame" , modDfObj, sep='\n')
'''
Delete multiple columns in dataFrame by Column Names
'''
print("**** Delete columns 'Age' & 'Name' from DataFrame")
modDfObj = dfObj.drop(['Age' , 'Name'] , axis='columns')
print("New Dataframe" , modDfObj, sep='\n')
'''
Delete multiple columns in dataFrame by Column Names
'''
print("**** Delete columns at Index Position 1 & 2 in DataFrame")
# Delete columns at index 1 & 2
modDfObj = dfObj.drop([dfObj.columns[1] , dfObj.columns[2]] , axis='columns')
print("New DataFrame with Deleted columns at Index position 1 and 2" , modDfObj, sep='\n')
'''
Delete multiple columns from dataFrame in Place
'''
print("Original Dataframe" , dfObj, sep='\n')
print("**** Delete columns 'Age' & 'Name' from dataFrame in Place")
dfObj.drop(['Age' , 'Name'] , axis='columns', inplace=True)
print("Modified DataFrame in place" , dfObj, sep='\n')
'''
Delete column if exist
'''
#Create a DataFrame object
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns = ['Name' , 'Age', 'City' , 'Country'], index=['a', 'b', 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f'])
print("Original DataFrame" , dfObj, sep='\n')
print(dfObj.columns)
# Check if Dataframe has a column with Label name 'City'
if 'City' in dfObj.columns :
dfObj.drop(['City'] , axis='columns', inplace=True)
else :
print('Column Name not found')
print("Modified DataFrame" , dfObj, sep='\n')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Output:
Original DataFrame
Name Age City Country
a jack 34 Sydeny Australia
b Riti 30 Delhi India
c Vikas 31 Mumbai India
d Neelu 32 Bangalore India
e John 16 New York US
f Mike 17 las vegas US
**** Delete column 'Age' in DataFrame object ****
New DataFrame
Name City Country
a jack Sydeny Australia
b Riti Delhi India
c Vikas Mumbai India
d Neelu Bangalore India
e John New York US
f Mike las vegas US
**** Delete columns 'Age' & 'Name' from DataFrame
New Dataframe
City Country
a Sydeny Australia
b Delhi India
c Mumbai India
d Bangalore India
e New York US
f las vegas US
**** Delete columns at Index Position 1 & 2 in DataFrame
New DataFrame with Deleted columns at Index position 1 and 2
Name Country
a jack Australia
b Riti India
c Vikas India
d Neelu India
e John US
f Mike US
Original Dataframe
Name Age City Country
a jack 34 Sydeny Australia
b Riti 30 Delhi India
c Vikas 31 Mumbai India
d Neelu 32 Bangalore India
e John 16 New York US
f Mike 17 las vegas US
**** Delete columns 'Age' & 'Name' from dataFrame in Place
Modified DataFrame in place
City Country
a Sydeny Australia
b Delhi India
c Mumbai India
d Bangalore India
e New York US
f las vegas US
Original DataFrame
Name Age City Country
a jack 34 Sydeny Australia
b Riti 30 Delhi India
c Vikas 31 Mumbai India
d Neelu 32 Bangalore India
e John 16 New York US
f Mike 17 las vegas US
Index(['Name', 'Age', 'City', 'Country'], dtype='object')
Modified DataFrame
Name Age Country
a jack 34 Australia
b Riti 30 India
c Vikas 31 India
d Neelu 32 India
e John 16 US
f Mike 17 US
This article is very helpful. Thank You!